Opioids are a class of medications used to treat pain. Natural opioids, semi-synthetic opioids produced from natural opioids, and synthetic opioids manufactured in a laboratory are all classified as opioids. Opioids are a class of medications that include opiates, which are naturally occurring compounds of the poppy plant. The primary distinction is that “opiate” refers to compounds produced from the opium (poppy) plant, while “opioids” include any molecules that interact with opioid receptors, including those manufactured in the lab.
Many semi-synthetic opioid medicines, such as heroin, oxycodone, and hydrocodone, are derived from naturally occurring opiate alkaloids, such as morphine, codeine, and thebaine.
Opioids drugs may be taken orally, injected, snorted, sucked, or absorbed via the skin or intestines. They are mostly used to treat moderate to severe pain. This might vary from treating acute back pain to treating fractured bones and cancer patients.
Some narcotics in moderate quantities, such as codeine, when combined with other analgesics such as paracetamol, ibuprofen, or aspirin, are intended to be available over-the-counter.These medications are used to treat severe headache , menstrual cramps, etc. that have not responded to simpler treatments.
Opioids are pain reliever that you get with a prescription. Opioids like Vicodin and OxyContin have been around for a while, but they come from very old sources. Prescription painkillers are made in labs, but they have the same structure as medicines found in nature. Opioids, in particular, are made from opium, which is the sap of poppy plants.
In Mesopotamia, about 3400 B.C., they developed the poppy strain responsible for the appropriate sap. It wasn’t until 1895 that poppy sap compounds were used to treat discomfort. In the past, people took opioids for fun.
Opioids mechanism of action?
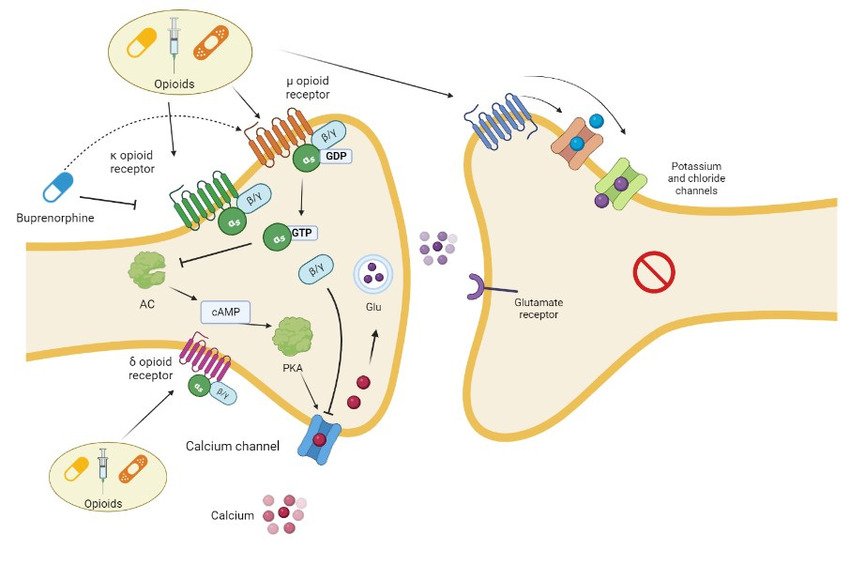
Attaching to receptors : There are opioid receptors in the brain, the spinal cord, and the gut. They look a bit like an electric plug. They are just waiting for painkillers to connect with them.
Triggering reactions: Each opioid works in a slightly different way, but they all cause dopamine to be released. People who use it feel happy and calm.
Causing tolerance: With continued use, you will need more of the drug to feel the same effects that smaller amounts used to give you.
Sparking dependence: Over time, people who use opioids can’t get dopamine out of their bodies without them. Without the drugs, they feel sad and sick to their bodies.
How Long Do Opioids Stay in your System?
People often want to know how long painkillers stay in your body after you stop taking them. It depends on a number of things, like:
- Your metabolism rate
- Your body weight and mass
- How long and how much you used opioids
- Your age
- The health of your liver and kidneys
- What kind and how well opioids are used
Depending on the above factors, an estimate can be given for each kind of opioid. You can expect the drug to be out of your system at some point within this range. But it’s important to remember that even though the opioids was no longer in your body, the effects of the addiction may still be there. Depression and hunger can last for a long time. In the same way, your organs won’t get better just because the opioid is no longer in your body.
Opioids stay in the body for different amounts of time. This varies on a number of things, such as the person’s age, general health, medical background, the type of painkillers they use, and how often they use them.
Opioids usually have a half-life of between 1 and 9 hours. For instance, oxycodone has a half-life of about 3.2 hours. On average, it can take between 18 and 24 hours for the body to get rid of all the opioids.
Dosage: The larger the opioid dosage, the longer it takes for the body to completely metabolize the medication. When someone abuses opioids, the medicines often linger in the system for a considerably longer period of time.
Age: Substances are normally metabolized more quickly in younger persons than in elderly people.
Frequency of use: The body develops a high level of tolerance if someone consumes opioids daily for many months or years. When compared to someone who uses opioids for just a short period of time, the medication will take longer to exit the body.
Physical fitness: The metabolic process may be impacted by heart, kidney, liver, and stomach problems. Unfortunately, a lot of opioid abusers are unaware that they have specific medical issues. Their ongoing drug usage might make their health issues worse.
How Long Do Opioids Remain in Hair, Blood, Saliva, and Urine?

Opioids of different strengths can be found with different tests. You might have to take a drug test because of your health, the law, or your job. Depending on the situation, failing these tests can definitely lead to very bad things.
Urine tests: Usually, opioids can be found in the urine for up to 3 or 4 days.
Blood tests: Most of the time, blood tests can find opioids for about 1-2 days.
Saliva tests: Usually, saliva tests can find opioids for 1 to 14 days.
Tests on the hair: Most hair tests can find opioids in the body for about 90 days.
Opioid Addiction Treatment
Once you’re done with rehab, you should think about taking a treatment plan to help your problem. Even though detox is an important first step on the path to recovery, opioid addiction treatment will help you change the way you think about opioids and opiates.
Because you’ve been taking these medicines for so long, your brain has been programmed to believe you need them to operate.
Plans for treating opioids include:
Outpatient care: There are different kinds of outpatient programs, but they all let the person stay at home while they are in treatment. Therapy and treatment are done on your time, so you can still go to work and do other things.
Partial hospitalization programs: In a partial hospitalization program, or PHP, you spend half your time in care and the other half at home. It includes both one-on-one therapy and group therapy, as well as other treatments and hobbies. People generally spend a few hours a day and a few days a week in PHP.
Addiction therapy: Individual and group therapy give you a chance to talk to a mental health expert about what’s on your mind and to share your experiences with opioids use with other people. What you say in therapy stays between you and your therapist.
How Opioids are metabolized
The process of metabolism decides how quickly a drug enters and leaves a person’s body. When taken by mouth, most opioids go through first-pass metabolism, which means that a large part of the opioid is broken down by the liver or stomach wall before it gets into the bloodstream. When a opioids is given intravenously or through the skin, it goes right into the bloodstream before it is processed.
Metabolites are byproducts of the metabolic process. Before they leave the body, they are generally connected with chemicals like glucuronic acid. But some chemicals are directly eliminated in the urine.
For opioids example, heroin is broken down by the liver, kidneys, brain, and heart into a drug called 6-monoacetylmorphine, or 6-MAM for brief. The body changes 6-MAM into morphine, and the liver metabolizes morphine. After morphine is broken down, the medicine is either released in the urine or feces as morphine, or it is linked to glucuronic acid and then expelled. 6-MAM can also be eliminated in urine or feces.
Since heroin breaks down into morphine, the appearance of morphine in a drug test can mean that the person used either heroin or morphine. Heroin is the only source of 6-MAM.
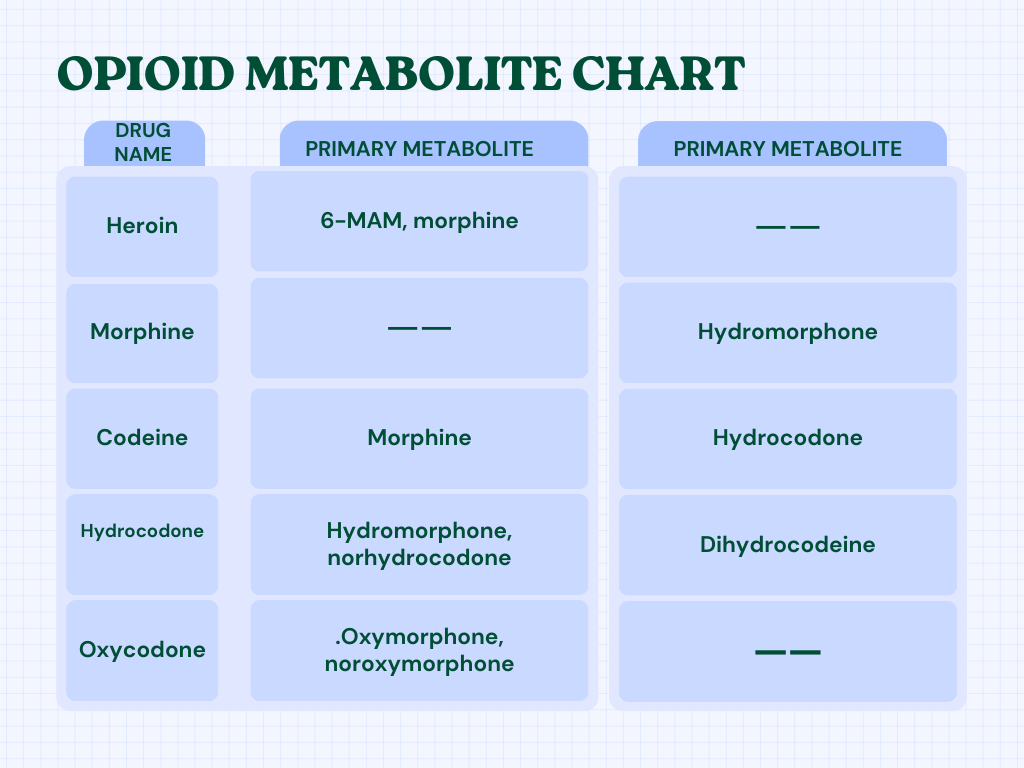
How strongly or weakly a opioids affects a person depends on how fast or slow their metabolism is For example, someone who has trouble metabolizing codeine might not feel its affects because the body only turns a small amount of the drug into the active metabolite morphine. On the other hand, people who quickly break down codeine can end up with a dangerously high amount of morphine in their blood.
Metabolism rates can change the results of drug tests. For example, someone with a high amount of morphine because their codeine is broken down quickly could be thought to be using heroin. But that doesn’t happen often.
FAQ:
1.What Types of opioids in this group ?
Opioids example: Buprenorphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphone, oxycodone, talpentadol, and pethidine are all controlled substances on Schedule 8 (S8).
2.What is a common opioids side effects ?
Most common side effects are expected because of how opioids work. These include nausea, vomiting, constipation, itching, dizziness, dry mouth, and sleepiness. Opioid treatment almost always causes side effects.
3.What should you not do while taking opioids?
Try not to take opioids with alcohol or other drugs or medicines. Mixing painkillers with other drugs, especially those that make you sleepy, is very dangerous: Benzodiazepines (like Xanax and Valium) Muscle relaxants, such as Soma and Flexeril
4.What is the greatest concern regarding opioid use?
Lower dosages of opioids may induce drowsiness, but higher doses can impair respiration and heart rate, leading to mortality. In addition, the pleasurable effects of opioids can lead to a desire to continue experiencing them, which can result in addiction.
5.Opioids vs Opiates ?
Opiates – painkillers that are made from opium poppies.
Opioids – painkillers that are at least part synthetic and not found in nature.
6. What are 3 symptoms of long term drug use from opioids?
Three symptoms of long-term opioid drug use are:
Physical Dependence: The body becomes reliant on opioids, leading to withdrawal symptoms when the drug is not taken.
Tolerance: Increasing amounts of opioids are needed to achieve the same effects, which can lead to higher doses and potential overdose risks.
Social Isolation: Long-term opioid use can result in withdrawing from social activities and relationships due to the focus on obtaining and using the drug
7. Is opioid damage permanent?
Opioid damage can be permanent, especially in cases of prolonged and excessive use, leading to lasting physical and cognitive effects.
8. What is the most serious effect of opioids?
The most serious effect of opioids is respiratory depression, which can lead to fatal overdose.
9. Do opiates affect liver or kidneys?
Yes, opiates can affect both the liver and kidneys, potentially causing damage over time.
10. Can you detect opioids in urine?
Yes, opioids can be detected in urine through drug tests.